Introduction :
With the emergence of new data sources, businesses have come to realize that structured data is not enough.
Traditionally, business used to tap into their structured data to derive their insights and make business decision.
But not anymore.
Now there is a growing thrust on leveraging unstructured data for deriving new insights into what the end users and customers think about your product, brand or store timings.
In the age of big data, unstructured data is the goldmine of actionable intelligence. Those who can unravel the unstructured data and use it for market research, price intelligence or any other business processes can achieve a definite competitive edge over others. Considering the potential that unstructured data offers, there is a growing research into how to capitalize on it.
Evidently, each data type – structured and unstructured- has something to offer for businesses but they need to be managed differently. You will need an in-depth understanding of the two data types and their various technical aspects so that you can make the most of both.
Before we get down to it, let’s try and understand what structured and unstructured data stand for.
Definition :
What is structured data?
Structured data refers to any data that resides in a fixed field within a record or file. This includes data contained in relational databases and spreadsheets.
Structured data is easy to enter, store, query, and analyze, but it must be strictly defined in terms of field name and type (numeric, currency, alphabetic, name, date, address) and any restrictions on the data input (number of characters; restricted to certain terms such Male or Female).
Structured data requires you to first create a data model. It is all about a model that defines the types of business data and how it will be stored, processed and accessed.
Structured data Examples :
- Meta-data (Time and date of creation, File size, Author etc.)
- Library Catalogues (date, author, place, subject, etc)
- Census records (birth, income, employment, place etc.)
- Economic data (GDP, PPI, ASX etc.)
- FaceBook like button
- Phone numbers (and the phone book)
- Databases (structuring fields)
What is unstructured data?
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is the kind of information that either does not have a predefined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner.
Unstructured data files at times include text and multimedia content. Email messages, word processing documents, videos, photos, audio files, presentations, web pages and many other kinds of business documents are some of the examples of such unstructured data files.
Some people believe that the term unstructured data is not accurate because each document may have its own specific structure or formatting based on the software that went on to create it. However, what is internal to the document is truly unstructured.
Unstructured data examples are as follows :
- Text files (Word processing, spreadsheets, presentations etc.)
- Email body
- Social Media ( Data from Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn)
- Website (YouTube, Instagram, photo sharing sites )
- Mobile data ( Text messages )
- Communications ( Chat, IM, phone recordings, collaboration software )
- Media ( MP3, digital photos, audio and video files )
Growth :
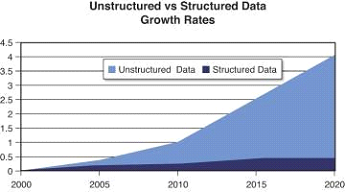
Unstructured data is growing at an astronomical pace. It is growing many times faster than the structured data.
About 20% of the total existing data is unstructured data.
With some research in unstructured data, analysts and data scientists have developed the view that organizations can capitalize on the insights derived from the unstructured data and achieve a competitive edge if they can devise ways to use advanced storage technologies.
In specific terms, eminent data analysts believe the following about unstructured data growth :
- IDG: Unstructured data is growing at the rate of 62% per year.
- IDG: By 2022, 93% of all data in the digital universe would be unstructured.
- Gartner: Data volume will grow 800% in the course of the next 5 years and 80% of it will be in the form of unstructured data.
Sources :
With the growth of technology, new sources of data have emerged in the last few years. This data is in large volumes and pose a challenge in terms of processing it.
The sources of data are divided into two categories :
- Computer or machine-generated
- Human-generated
Computer or machine-generated :
Machine-generated data generally refers to the kind of data that is created by a machine without human intervention.
| Machine Generated Structured Data sources | Machine Generated Unstructured Data sources |
|---|---|
| Sensor data: When you talk about radio frequency ID tags, smart meters, medical devices, and Global Positioning System data, you are basically referring to machine generated structured data. Supply chain management and inventory control is what gets the companies interested in this. | Satellite images: When you take into consideration the weather data or the data that government agencies procure through its satellite surveillance imagery, you are talking about machine generated unstructured data. Google Earth and similar mechanisms aptly illustrate the point. |
| Web log data: When systems and mechanisms such as servers, applications and networks etc. work, they soak in different types of data regarding whatever is the operation. It means enormous piles of data of diverse kinds. Based on this data, you can deal with service-level agreements or predict security breaches. | Scientific data: All scientific data that includes seismic imagery, atmospheric data and high energy Physics so and so forth stand for machine generated unstructured data. |
| Point-of-sale data: When the digital transactions take place over the counter of a shopping mall, the machine captures a lot of data. This is machine generated structured data related to barcode and other relevant details of the product etc. | Photographs and video: When machines capture images and video for the purposes of security, surveillance and traffic, the data that is produced is machine generated unstructured data. |
| Financial data: Computer programs are used with respect to financial data a lot more now. Processes are automated with the help of these programs. Take the case of stock-trading. It carries structured data such as the company symbol and dollar value. A part of this data is machine generated and some of it is human generated. | Radar or sonar data: This includes vehicular, meteorological, and oceanographic seismic profiles. |
Human-generated :
This is data that humans, in interaction with computers, supply.
| Human Generated Structured Data sources | Human Generated Unstructured Data sources |
|---|---|
| Input data: When a human user enters input such as name, age, income, non-free-form survey responses etc. into a computer, it is human generated structured data. Companies can find this type of data quite useful in studying customer behavior. | Text internal to your company: This is the type of data that is restricted to a given company such as documents, logs, survey results, emails etc. Such enterprise information forms a big part of such unstructured text information in the world. |
| Clickstream data: This is the type of data generated through the process of a user clicking a link on a website. Businesses like this type of data because it allows them to study customer behavior and purchase patterns. | Social media data: This kind of data is generated when human users interact with social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Flickr, YouTube, LinkedIn etc. |
| Gaming-related data: When a human user makes a move in a game on a virtual platform, it produces a piece of information. How users navigate a gaming portfolio is a source of a lot of interesting data. | Mobile data: This type of data includes information such as text messages and location information. |
| Website content: This type of data is derived from a site delivering unstructured content such as YouTube, Flickr, Instagram etc. |
Characteristics :
Each data type behaves differently when weighed against a set of qualities or characteristics. When one approaches data from the point of view of different characteristics such as flexibility, robustness, accessibility etc. one begins to understand how each data type differs.
Since by nature both data types are distinct from each other, they will fare completely differently with respect to these characteristics. For instance, when it comes to structured data, scaling DB schema is difficult but for unstructured data, it is highly scalable. Hence, until and unless we understand the different characteristics and compare the two data types against these characteristics, it would not be possible to fully grasp the difference between structured and unstructured data.
Therefore, it would be advisable to take a look at how the characteristics of two data types and the way they differ in the context of these characteristics.
| Structured data | Unstructured data | |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Schema dependent rigorous schema | Absence of schema, Very flexible |
| Scalability | Scaling DB schema is difficult | Highly scalable |
| Robustness | Robust | – |
| Query Performance | Structured query allows complex joins | Only textual query possible |
| Accessibility | Easy to access | Hard to access |
| Availability | Percentage wise lower | Percentage wise higher |
| Association | Organized | Scattered and dispersed |
| Analysis | Efficient to analysis | Additional preprocessing is needed |
| Appearance | Formally defined | Free- From |
Storage Techniques :
Note: Storage architecture actually hinges upon each distinct use case.
Here’s how general architecture looks like :
Structured data storage technique :
Block storage / block level storage :
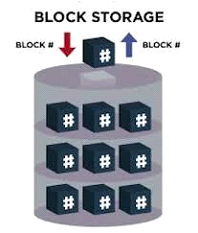
This type of data storage is used in the context of storage-area network (SAN) environments. In such environments, data is stored in volumes which is also referred to as blocks.
An arbitrary identifier is assigned to every block. It allows the block to be stored and retrieved but there would be no metadata providing further context.
Virtual machine file system volumes and structured database storage are the use cases of block storage.
When it comes to block storage, raw storage volumes are created on the device. With the aid of a server-based system, the volumes are connected and each one is treated as an individual hard drive.
Unstructured data storage technique :
Object storage :
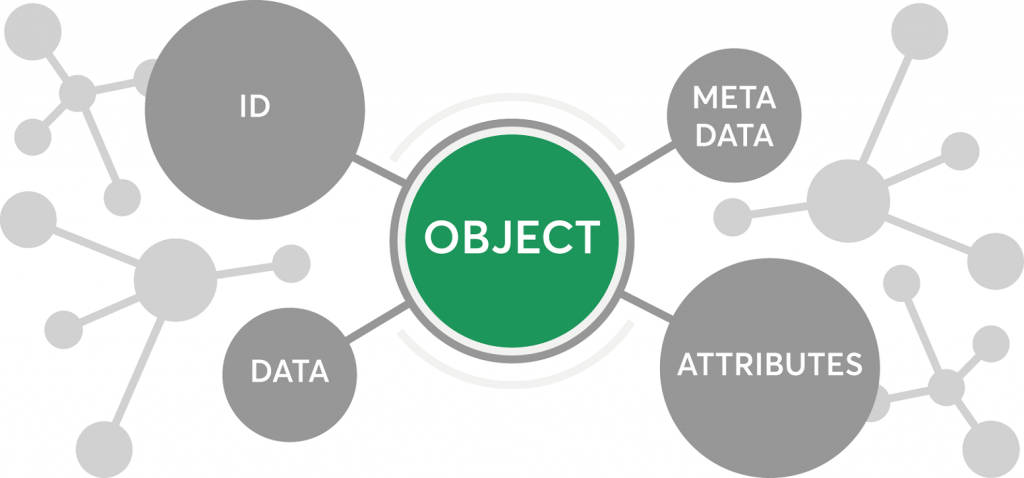
This particular technique is basically a way of storing, organizing and accessing data on disk. The difference however is that it is done so in a more scalable and cost-effective manner.
This kind of storage system makes it possible to retain huge volumes of unstructured data. When it comes to storing photos on Facebook, songs on Spotify, or files in collaboration services such as Dropbox, object storage come into play.
Each object incorporates data, a lot of metadata and a singularly unique identifier. This kind of storage can be done at different levels such as device level, system level and interface level.
Since objects are robust, this kind of storage works well for long-term storage of data archives, analytics data and service provider storage with SLAs linked with data delivery.
Data storage and Management Tool :
Structured Data Storage and Management Tool :
Structured Query Language (SQL), a programming language devised for managing and querying data in relational database management systems, is often used in managing structured data.
Here’s how you can store and mange data using some of the different tools :
Oracle RDBMS :
- Oracle database has the distinction of being the universally used object-relational database management software. Oracle Corporation produces and markets it.
- Oracle is quite secure. It does not occupy huge amount of space. It is good at supporting large databases. It also reduces CPU time to process data.
Microsoft SQL Server :
- Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system. As the name indicates, it was created by Microsoft.
- As a database server, it is basically a software product whose primary function is to store and retrieve data that is requested by other software applications. These applications may run on the same computer or some other computer on some other network. It could be on the Internet.
MySQL :
- Compared to the Microsoft product, MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS).
- MySQL is capable of powering the intricate and powerful web, e-commerce, SaaS and Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) applications.
Unstructured Data storage and Management Tool :
Unstructured data contains a lot of information that can be leveraged. Businesses can use the information contained in emails, social media postings etc. to derive operational intelligence, marketing intelligence etc.
Customer surveys are not enough for sentiment analysis and businesses need to go beyond the same to work out new ways to study customer behavior. Unstructured data can be of immense help in this regard.
However, you need to bear in mind that unstructured data is basically different and does not fit into any of the traditional tools like relational databases. Searching it based on the existing algorithms is not quite a viable exercise.
Let’s say if it was easy or possible to process it, it would become structured data and then it would become easy to derive actionable intelligence from it in the same way. But it is not so.
However, there are some tools that you can use to store and manage unstructured data :
Hadoop :
- Since it is an open source software framework, Hadoop has distributed storage and distributed processing framework. Considering the size and complexity of unstructured data, such a system is quite important for unstructured data analysis.
Amazon web Service S3 :
- Amazon web service S3 is useful because it provides cloud storage in order to allow you to leverage an object-storage architecture.
IBM Spectrum Scale :
- It is basically distributed file systems that makes use of object-based architecture. In it, file metadata is stored in metadata servers whereas file data is stored in object storage servers. The file system client software which is in place gets into interaction with the distinct servers and gets them to present a full file system to users and applications.
Semi Structured Data :
As the name suggests, this type of data is something between structured and unstructured data. It carries aspects which are structured and some others which are not structured.
Overview :
Semi-structured data is not entirely unstructured but it stands for a form of structured data that does not align with the formal structure of data models that one associates with relational databases or other forms of data tables. Notwithstanding any of this, it still contains tags or other markers to distinguish semantic elements and ensure the systematic hierarchies of records and fields with the data. Hence, there are some who call it self-describing structure.
With respect to semi-structured data, one should remember that entities falling in this category may have different aspects although they are placed together under this category. Moreover, the sequence of these attributes may not be important.
Type of semi structured data :
XML ( eXtensible Markup Language) :
- XML is a typical example of semi-structured data. It is actually a language for data representation and exchange on the web.
- In XML, data can be directly encoded and a Document Type Definition (DTD) or XML Schema (XMLS) may define the structure of the XML document.
- XML can be said to be having “flexible structure” that is capable of human-centric flow and hierarchy as well as highly rigorous element structure and data typing.
JSON :
- JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is an open standard format that uses human-readable text to transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs.
- It is utilized primarily to transmit data between a server and web application, as an alternative to XML. JSON has been popularized by web services developed utilizing REST principles.
The Bottom Line :
It is irrelevant what your business is about; what matters is how you leverage data whether it is structured or unstructured.
Both types of data can help you capitalize on new insights that you can derive by processing it. It will depend on your understanding of what each type of data stands for and how to decode it.
If you can leverage it, whether structured or unstructured, you can open up the universe of possibilities regarding how you can accelerate the growth of your business!